29 août 2024
The degradation of agricultural soils : a global challenge
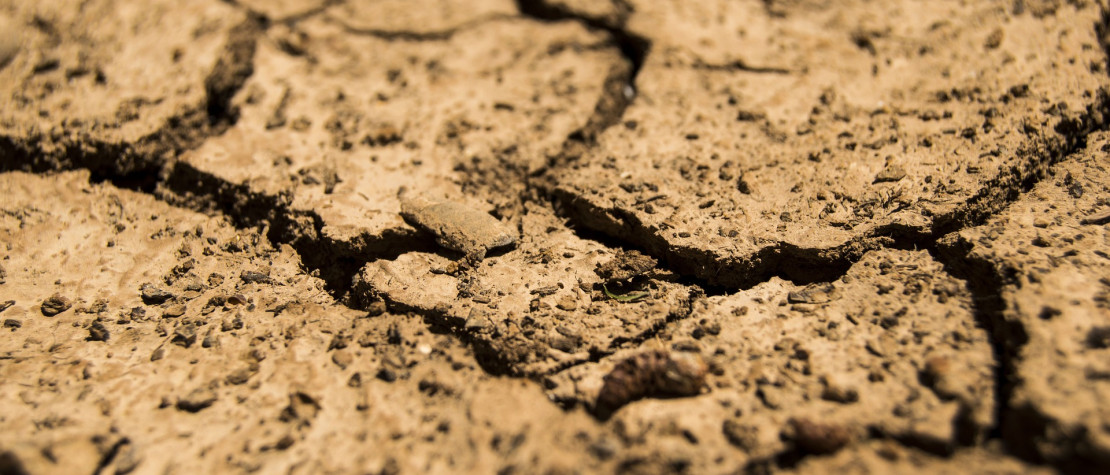
In just a century, we have caused more soil degradation than in the previous 1,000 years combined. This alarming figure reveals a worrying trend that requires immediate and coordinated action from all stakeholders. UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) issued a warning last July: "Soils play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. Yet, they are still often neglected or poorly managed."
How did we get here?
The degradation of agricultural soils is largely due to intensive and unsustainable practices such as intensive monoculture, excessive use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, and intensive plowing. These practices have compromised the physical structure, biodiversity, and natural fertility of soils. As a result, soils are now less capable of supporting sustainable crop growth, leading to decreased yields and increased agricultural instability.
Degraded soils, what risks ?
The consequences of soil degradation are numerous, affecting the environment, economy, and global food security.
First, the decline in soil fertility leads to reduced agricultural yields. When soils lose their ability to supply essential nutrients to plants, this results in a significant decrease in agricultural productivity. This drop directly impacts farmers, whose income depends on their production, and jeopardizes the food security of millions of people.
Lower agricultural yields also lead to higher production costs, as farmers are forced to invest more in fertilizers and inputs to compensate for the loss of natural fertility. Ultimately, this leads to higher food prices.
Soil degradation also has a direct impact on the climate. Soils are natural carbon reservoirs, and when they degrade, this carbon is released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. This release contributes to climate change, creating a vicious cycle where extreme weather conditions, such as droughts and storms, further accelerate soil degradation. Furthermore, degraded soils lose their ability to retain water, reducing ecosystems' resilience to droughts.
Revitalizing our agricultural soils : the importance of organic fertilizers
In the face of this global crisis, it is imperative to promote sustainable agricultural practices and restore soil health. Organic fertilizers, such as Germiflor® products, play a crucial role in this restoration process.
Unlike chemical fertilizers, which can alter soil structure in the long term and destabilize ecosystems, organic fertilizers enrich soils with organic matter, essential nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms. They also improve soil structure, increase its water retention capacity, and thus reduce the need for irrigation. Moreover, organic fertilizers promote the biodiversity necessary for healthy soil balance and reduce erosion, thereby contributing to the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems.
Germiflor® fertilizers go even further by offering a unique synergy, combining the benefits of an organic amendment with a means of biological control. This innovation, supported by the CRONOPS® patent, provides our MAZOR® plant-based formula with unprecedented functionalities, allowing it to nourish the soil while providing protection against diseases.
---
At a time when soil preservation and restoration are becoming global priorities, Germiflor® products position themselves as a reference solution. By investing in environmentally friendly solutions and raising farmers' awareness of the importance of soil health, we can together build a more resilient and sustainable future for our agriculture.